Calcium is undoubtedly, the most essential vitamin in your body. More than 99% of the calcium in your body is stored in your bones and teeth, which supports skeletal function and structure.
The remaining calcium in your body is needed for other vital processes such as muscle contraction, blood vessel contraction and expansion, and nervous system communication.
Despite the fact that it is one of the most important minerals for your health, most individuals do not receive enough of it. According to one research, up to 68% of the American population is calcium deficient.
Adolescent girls and boys, women over 50, and men over 70 are all in danger of not getting enough calcium in their regular diet. Calcium deficiency is more common in menopausal women, vegetarians, and people who have a dairy allergy than in the general population.
12 Signs Your Body Desperately Needs It

What is Calcium Deficiency (Hypocalcemia)?
Hypocalcemia is a condition in which the blood calcium levels are abnormally low. Symptoms can range from moderate and imperceptible to major and life-threatening, depending on the severity. Acute and chronic calcium insufficiency are both possible.
The most important mineral in your body is calcium. It is necessary for the bones, heart, muscles, and neurological system to function properly. Calcium is required by every cell in your body! However, only around 1% of your calcium is present in your blood, with the rest being stored in your bones and teeth.
Keep in mind that blood calcium levels often decline owing to non-dietary factors, rather than dietary calcium insufficiency.
Calcium Blood Test
A calcium test determines the amount of calcium in your blood. The test most often measures your total serum calcium, which includes:
- Calcium linked to proteins, primarily albumin (40–45%)
- Phosphate and citrate complexed calcium (about 10%)
- Ionized calcium, typically known as free or active calcium (about 45–50%)
An ionized (free) calcium test may also be ordered by your doctor. The active form of calcium in your body is ionized calcium. It is estimated to account for 45 – 50% of total blood calcium. However, the actual percentage may vary.
Total blood calcium and albumin levels are frequently used to determine ionized calcium levels. Ionized calcium testing is significantly more exact, but it needs specialized equipment and is costly.
Signs and Symptoms of Calcium Deficiency
Your body communicates with you in some manner. It notifies you of critical and non-critical circumstances, allowing you to take preventative actions and save money on hospital bills. When calcium levels in the body are low, a deficiency disorder known as ‘hypocalcemia’ arises.
If the disease is not treated, it can become life-threatening and even fatal.
If you’ve been suffering any of the following signs and symptoms, it’s likely that your body is short on calcium and needs to be replenished as soon as possible.
1. Muscle Cramps
You’ve been fast asleep for a while when the pangs start. They assault the calf muscles of the leg and cause agonizing pain throughout the body, causing you to wake up. The rest of the night is spent stretching and massaging. This is a common technique for your body to alert you to a calcium deficiency. You may accomplish this by drinking a glass of milk and eating other calcium-rich meals.
2. Numbness and Tingling
Tingling in the extremities, particularly the hands and feet, is another common sign of hypocalcemia. Numbness can also be caused by a severe deficit. Every nerve cell in your body needs calcium. Nerve cells struggle to register feelings and deliver impulses when calcium levels fall too low.
3. Fatigue
Fatigue can be caused by hypocalcemia. Calcium is required for muscle fibers and neurons, hence its depletion in cells causes weariness, exhaustion, and weakness.
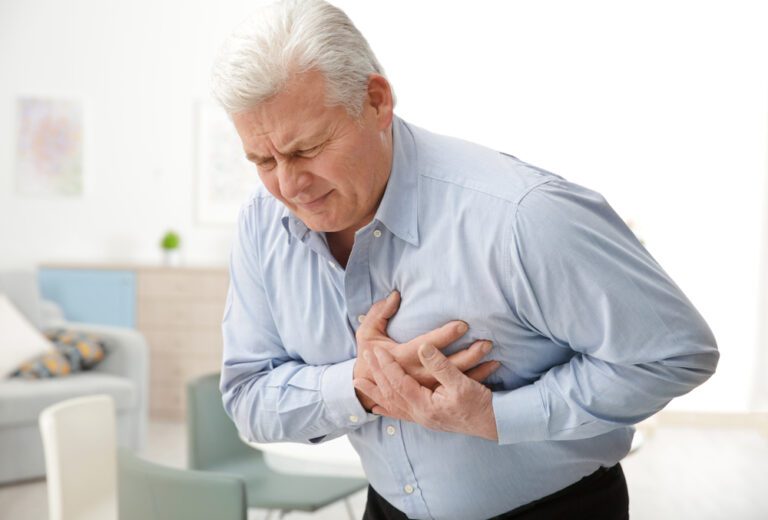
4. Abnormal Heart Rhythm
Irregular heartbeat is a common symptom of hypocalcemia, and it can be dangerous if it is severe. It typically results in a number of anomalies that may be detected by an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Given that the heart is a muscle, it’s no wonder that calcium insufficiency might cause problems. When cardiac cells do not receive enough calcium, they cease performing properly. This can disrupt the regular cardiac rhythm, produce heart muscle spasms, and restrict the arteries.
5. Seizures
Calcium is required for the release of neurotransmitters by brain cells and for muscular contraction by muscles. Hypocalcemia can cause the brain to become too excited, resulting in seizures.
6. Osteopenia & Osteoporosis
A calcium shortage condition can result in osteoporosis or brittle bones. Osteopenia is a kind of osteoporosis that is less severe. When calcium levels in the blood decline, the body must adjust by releasing more calcium from the bones. Calcium shortage can lead to significant bone fragility, frailty, and an increased risk of fractures over time.
7. Dry skin
Hypocalcemia can manifest itself in the form of dry or scaly skin. Calcium plays a lesser-known role in skin health by lowering the pH of the skin and protecting the skin barrier. This stops the skin from losing too much water. When calcium levels in the blood drop too low, the skin loses its ability to retain moisture and a balanced pH.
8. Confusion and Memory Loss
Hypocalcemia can cause confusion, disorientation, and memory loss, among other things. Calcium is required by nerve and brain cells. Calcium promotes the release of neurotransmitters when it enters nerve cells. A calcium shortage has been shown to have a major impact on cognitive performance.
9. Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is exceedingly frequent, for a wide range of reasons. According to a major evaluation of 28 studies, low levels of vitamin D and calcium can either cause or contribute to the symptoms. Vitamin D and calcium can help to alleviate or even eliminate PMS symptoms in such circumstances.
10. Tooth Decay and Gum Disease
Calcium helps to keep your teeth healthy. Minerals in the teeth can be degraded by food, beverages, and oral germs. Calcium levels must be adequate to prevent this mineral loss. Furthermore, research indicates that calcium shortage is one of the causes of gum disease.
11. Rickets
Rickets in children can be caused by a lack of calcium (or vitamin D). Calcium shortage impairs adequate bone mineralization, which is critical for a growing youngster. Bones become weak and brittle, and abnormalities are possible. Rickets is very uncommon in the industrialized world.
12. Depression
Some evidence shows that calcium insufficiency may be connected to mood disorders, including depression, although further study is needed to prove this.
If you feel like a calcium deficit is contributing to depressive symptoms, you should see a doctor. After a calcium level check, the doctor may recommend a calcium supplement.





















2 thoughts on “Calcium: 12 Signs Your Body Desperately Needs It”
Thank you
How do you know how much calcium to take