How many things do YOU know about SPF protection? Are you using it correctly?
Summer is just around the corner and finding a 100% effective SPF protection cream is mandatory. But before rushing to the closest supermarket to get it, you must know a few things about all these protection creams.
A recent study found that 80% of sunscreens either contain dangerous substances or provide very low protection against the whole spectrum of UV light. To what extent should you be concerned?
Multiple investigations indicate that U.S. sunscreens are not as effective against one type of ultraviolet (UV) radiation and that improper or careless application, which is promoted by the delusion of security that ultra-high SPF ratings provide, may reduce the effectiveness of sunscreen.
Without further ado, let’s see what are the downsides of SPF protection lotions:

1. A lot of them contain harmful ingredients
Sunscreen and sunblock creams unquestionably help stop sunburn and skin harm. Applying topical sunscreen, often known as sunscreen lotion, can help shield delicate skin from the sun’s damaging rays, which can cause skin cancer, aging, and blistering.
Now, nothing strange, but after a ton of research conducted on this matter, retinyl palmitate, a kind of vitamin A, and oxybenzone, two typical ingredients found in most sunscreens, are suspected to be dangerous.
Oxybenzone functions in the body similarly to a hormone and can pass through the skin. The molecule is present in the blood of more than 95% of individuals at any given time, and summertime is when levels are highest.
Certain products don’t contain oxybenzone, even though many do. If you want to stay away from oxybenzone, there are many choices available to you. You just have to read the label carefully before buying.
2. …and not Oxybenzone is harmful there is also…
It has also been demonstrated that vitamin A (retinal) and its derivatives, such as retinol and retinyl palmitate, in sunscreen lotions are photo-unstable. Numerous well-known sunscreen creams include vitamin A or its derivatives, which may potentially worsen skin damage, according to current studies.
Sunscreen may be causing more harm to the skin than it is supposed to shield! Note: This also applies to sunscreen- and/or vitamin A-containing creams and cosmetics.
3. SPF doesn’t represent UVA protection
The bigger the SPF protection, the better right? Uhm…not so much. Let’s see why. The Sun Protection Factor, or SPF, does not indicate how well a sunscreen blocks UVA radiation; it solely describes UVB protection.
The degree of UVA coverage may be uncertain since UVA protection is not measured by SPF, despite promises made by sunscreen brand lotions to be “broad spectrum” or to protect against both UVB and UVA radiation.
To put it another way, a sunscreen with an SPF of 50 could or might not offer significant UVA protection. Because of this, you might believe that a high SPF can protect you completely, but in reality, it will just make you spend more time in the sun and cause more serious UVA damage to your skin!
Moreover, studies reveal that SPF tests for high-SPF sunscreens can be unstable and that sunscreens with an SPF of more than 30 don’t provide any extra protection. Furthermore, correctly applied SPF 30 sunscreen blocks 94% of UVB radiation; at SPF 50, that percentage jumps to 97%.
4. If you have acne using an SPF protection cream can make it worse
Certain chemicals in sunscreen can worsen acne if you are prone to this skin condition. By utilizing non-comedogenic and non-oily sunscreens, you may prevent this negative effect of sunscreen.
Your skin type should be taken into consideration while choosing sunscreen, and if you are not sure which one is good for you, ask your dermatologist. Furthermore, because they are excessively thick, sunscreen for the body shouldn’t be applied to the face.
Do you suffer from acne? Find out with your physician if the Neutrogena sun lotion is right for you. If so, it’s readily available on Amazon for just $8.08, a very reasonable price, and only requires one click.
5. Increases the chance of developing breast cancer
Certain chemicals in sunscreen have the potential to stimulate estrogenic responses in breast cancer cells. Blood estrogen levels may be impacted by certain sunscreens.
Children should not use chemical sunscreens since their skin absorbs the chemicals more quickly. Chemical sunscreens frequently contain benzophenone-3 as one of their ingredients. It accelerates the growth of tumor cells and encourages breast cancer.
For you to understand better there were conducted plenty of research on mice and the application of BP-3 raised the percentage of epithelial cancers in mice given an adult-restricted diet rich in saturated animal fat (HFD).
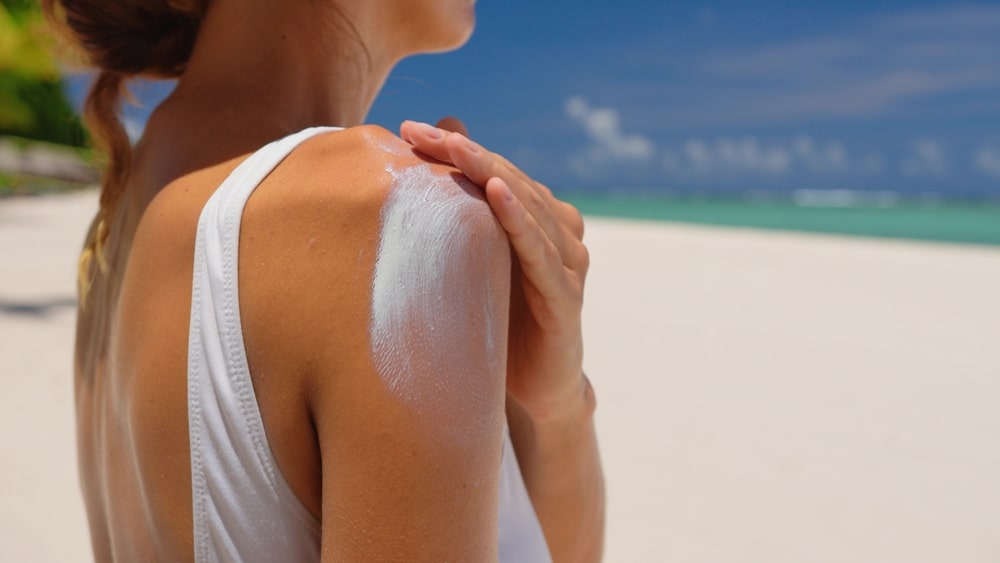

6. You may not use your SPF protection correctly
Although it may not be clear to you why, you’ve probably heard plenty of times that you should reapply sunscreen every two hours. A substance called avobenzone, one of the most widely used UVA blockers in sunscreens, degrades in the sun.
According to a study, just one hour of sun exposure reduces the efficiency of avobenzone by 50–60%. Even if producers combine it with other compounds to stabilize it, it ultimately degrades and becomes less effective.
When combined with other types of UV protection, sunscreen offers the greatest level of protection. Using sunscreen on its own isn’t sufficient.
Wear lightweight clothing, cover your head with a hat (ideally a straw one), and, last but not least, protect your eyes with a pair of sunglasses (available at optical stores). Sunscreen doesn’t work like a shield or an armor especially if isn’t applied correctly!
Make sure you use a good amount of SPF protection. An adult, for instance, has to apply around one teaspoon of sunscreen to each area of their body, or about 35 mL for the entire body.
Each arm, limb, and the front and back of the body should receive the same quantity, as should the face, neck, and ears. Don’t forget that any SPF lotion needs around 20 minutes to work accordingly. And of course, every two hours, you need to reapply.
Bottom line:
After you find out all these important things about SPF protection is even more crucial to read the labels before you buy them but you also make sure you’re using them every time you go out of the house, especially during the summer and if you’re living in a state with tropical climate.
Experts advise using a zinc oxide lotion, or a combination of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide since this provides full-coverage (UVA and UVB) sun protection.
Additionally, zinc oxide doesn’t appear to cause any health risks, and research has shown that it is far more photo-stable than other conventional chemical sunscreens. But be careful that the item you use doesn’t include any of the possibly harmful substances covered in the preceding sections!
How many times did you forget to use sunscreen, and most importantly, what brands do you use? We hope this article will be helpful, and from now on, you will make only wise choices to protect yourself and your family.
If you enjoyed this article, we’d be very grateful if you’d help it spread by emailing it to a friend or sharing it on Twitter or Facebook. Thank you!
Related post: 8 Common Carcinogens You Might Find in Skincare Products.