What do you know about salmonella poisoning?
According to a recent statistic made by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in the U.S. there are around 1.35 million cases of salmonella poisoning, from which 420 deaths and 26,500 people get in the hospital.
With these alarming numbers, each of us must know a bit more about this illness, how to prevent it, and, in case you catch it, how you can identify it before going to the doctor. Salmonella can infect anyone, but it is more likely for children under five, infants not breastfed, older adults, and those with weak immune systems to get it.
…But what is salmonella exactly?
For those who aren’t exactly familiar with this illness, salmonella is a bacteria that lives in the intestines, and it’s thrown out when we poop. Salmonellosis is a bacterial infection that may spread to people when they consume contaminated food or water. The first thing that hurts when you have salmonella is your stomach.
When the bacteria enter the body, the water you consume will no longer be fully absorbed, leading to terrible stomach cramps. Since the body doesn’t absorb the water properly, it will leave it quickly in the form of diarrhea.
In most cases, if you get salmonella poisoning, you will experience the symptoms in a couple of hours, and with the right treatment, you will get better within four to seven days.

Symptoms of salmonella poisoning
As we previously mentioned, the first symptoms of salmonella poisoning show up pretty quickly a couple of hours after you get infected. In most cases, symptoms are pretty much the same, but in some people, they’re manifesting extremely badly. Since salmonella is mainly caused by eating eggs or dishes made with eggs that weren’t cooked accordingly, or meat and poultry, many people confuse stomach aches with a simple flu.
Some of the most common symptoms that can appear in the first six hours after the patient ate the contaminated food are diarrhea, which sometimes can be bloody; stomach cramps; nausea; vomiting that prevents you from eating and keeping liquids down; a fever higher than 102 degrees Fahrenheit; and unbearable headaches.
If you experience at least two of these symptoms after you consume some foods mentioned above, please contact your doctor.
How it’s diagnosed?
Your doctor will need to collect a stool or blood sample and perform a laboratory test to confirm a case of salmonellosis. Antibiotics may be necessary if the infection spreads from the intestines to the bloodstream and then to other parts of the body, but most people recover without any additional medication
Can salmonella poisoning be treated, or does it go away on its own?
If the doctor knows that the salmonella poisoning isn’t that bad, then you’re lucky, and they won’t prescribe you any medication. In case the diarrhea is more severe and that could lead to serious complications, you might need hospitalization for a couple of days.
It’s important to stay hydrated throughout the day because the majority of patients who have salmonella poisoning are dehydrated. In case the illness doesn’t go away on its own, besides antibiotics like Ciprofloxacin or Azithromycin, your doctor may also prescribe intravenous fluids.
Since salmonella poisoning is on the rise in the United States, you might want to be careful and take all the precautionary measures to make sure you and your family are staying safe.
Medical personnel recommend that everybody should have a Bacteria Water Test Kit for Drinking Water that can detect any type of bacteria found in water, from E. coli to salmonella, in less than 15 minutes.

Are there any complications of salmonella poisoning?
As we previously mentioned, salmonella usually goes by itself, and most patients don’t need antibiotics to treat it. If you keep yourself hydrated by drinking sports drinks that contain electrolytes, water, and fruit juice without sugar added when the first symptoms appear, you should be able to get better in a couple of days.
However, even though the majority of people do not experience salmonella complications, you should be alert for any indications of a more serious illness. Reactive arthritis, osteomyelitis, and bacteremia are a few of the side effects of salmonella.
Diseases derived from salmonella poisoning complications:
Bacteremia is the first side effect of salmonella and when this happens the virus will begin infecting other organs and tissues if it enters your bloodstream.
Your bones, joints, brain lining, heart, or heart valves may become inflamed as a result of the infection. Moreover, bacteremia can cause sepsis, a potentially fatal illness in which your body is attacked by your immune system.
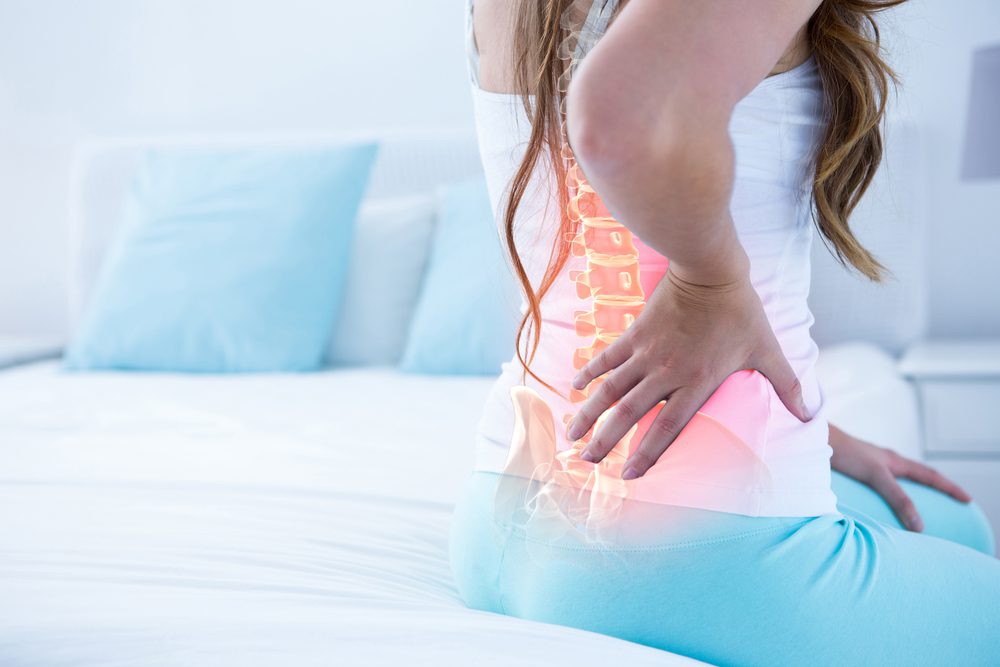
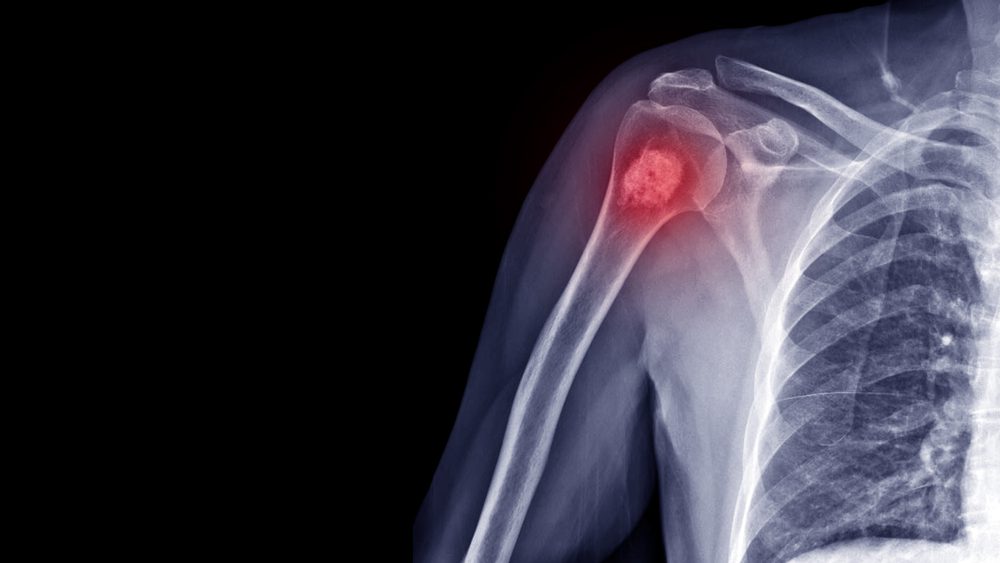
Salmonella osteomyelitis is the second one, and it usually develops if you’re living with sickle cell disease. Consult your doctor if you have had salmonella and have bone or back pain, discomfort that limits movement, or body parts that are red, swollen, or filled with fluid.
Reactive arthritis can happen when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy parts of the body when it’s trying to fight an illness. Your eyes, joints, and lower back become inflamed when you have reactive arthritis. Frequent urination, lower back pain, joint pain, stiffness and swelling, diarrhea, and abdominal pain or conjunctivitis are all signs of reactive arthritis.
Although it’s not required, some people also develop rashes all over their bodies. However, you must see a doctor right away if you experience even one or two of the symptoms listed above.
Bottom line:
Keep in mind that you can also get salmonella from people who are infected with it. It may sound surreal, but it can be transmitted through a simple touch of a hand. And if after that you accidentally touch your mouth, then… voila! You got it too. Furthermore, contaminated food doesn’t have a different smell or look unusual, so you can’t really say outright if it’s good or bad.
Because of the warmer temperatures, salmonella illness is more prevalent during the summer season. This is the perfect environment for the bacteria to flourish and that occurs when perishable foods are not stored in the refrigerator at optimal conditions. Cooked dishes, leftovers, and perishables should all be kept in the refrigerator or freezer within two hours to avoid the risk of contamination.
Furthermore, when you prepare your food, wash thoroughly your fresh fruits and veggies and keep them as far away as possible from raw meat. Never cut the meat and the vegetables with the same knife! Of course, it goes without saying that washing your hands both before and after cooking is a crucial step in maintaining food safety.
Although it’s very unlikely, salmonella can kill you if it spreads to other parts of your body or results in sepsis. As we mentioned at the beginning of the article, in the United States, Salmonella causes millions of infections annually, but only 420 of those infections result in death.
Are you interested in more health-related articles? Subscribe to our page and you can get everything we write straight to your email. And if you change your mind, you can unsubscribe at any point for free! Meanwhile, you may be interested in reading about the COVID-19 new strain.